PMP® Exam Questions - The Complete Guide

Practice makes perfect. If you were a baseball player, you don’t want to be up at the bat only to strike out. You may practice against a teammate to improve your swing, but ultimately, there is no real substitute for playing a real game. When you play a competitive sport, after all your hard work in preparing and training, you want to win. It is the same with the Project Management Professional (PMP)® exam. A PMP® credential is an important one to advance in your career. On the day of the PMP® exam, when you are at the PMP exam center, you want to pass!
To ensure your success, you need to know the PMP® Examination Content Outline (ECO), project management best practices described in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) and and other PMI reference materials, and, most importantly, take as many PMP practice exams as possible. In this article, I describe the most common types of PMP questions, provide you with sample PMP questions and give you links to where you can get more free PMP exam questions.
Read this article and find out more about how PMP sample questions can help you pass your PMP exam.
- Chapter 1PMP Exam Question Format and Types
- Chapter 2Situational or Scenario-Based PMP Exam Questions
- Chapter 3Knowledge-Based PMP Exam Questions
- Chapter 4Watch this Video with a Knowledge-Based Sample PMP Exam Question
- Chapter 5Interpretational PMP Exam Questions
- Chapter 6Technique-Based PMP Exam Questions
- Chapter 7Formula-Based PMP Exam Questions
- Chapter 8My Top 10 Recommended Web Sites for Free PMP Exam Questions
- Chapter 9The Next Step for PMP Certification Exam Prep
- Chapter 10Learn More about PMP Exam Questions
- Chapter 11Conclusion and Recommendation: Use a PMP Exam Simulator
PMP Exam Question Format and Types
"How much practice do I need?" A good rule of thumb is that you should be able to repeatedly answer 70% or more sample questions in a full practice exam correctly on your first try.
The PMP exam is composed of 180 mostly multiple-choice questions (more about the different question formats in a second), which are distributed throughout the three ECO domains: People, Process, and Business Environment. Additionally, as the ECO states, "About half of the examination will represent predictive project management approaches and the other half will represent agile or hybrid approaches." A test taker is allotted 230 minutes to complete the exam (with two 10-minute optional breaks after answering the 60-th and the 120-th question).
To prepare for the PMP exam, you should familiarize yourself with different PMP exam question formats and types. A typical PMP exam question contains 4 choices, of which there is only one correct or best answer. Other question formats include multiple response, drag-and-drop, fill-in-the-blank, and hotspot. A multiple-response question may have more than 4 answer choices, and more than one choice being the correct answer. Drag-and-drop questions require a test-taker to match pairs. To answer the fill-in-the-blank question, the test taker has to select the answer choice that, as the name implies, best fills the blank spot in the scenario. And finally, a hotspot question is typically an image where the test taker should click the spot representing the correct answer. But don't worry - our PMP Exam Simulator has them all!
In this article, I describe the most common types of PMP questions. These are the situational (or scenario-based), knowledge-based, interpretational, and formula-based questions. For each type, I also provide a sample question. For each sample PMP exam question, I include a hint, the correct question and an explanation. Note that on an actual PMP exam, there is no hint and (obviously!) no correct answer or explanation.
Therefore, I urge you to use this knowledge of the PMP exam question types in order to be more proactive in your PMP exam preparation. When you study the PMBOK® Guide or other PMI reference materials, ask yourself. “How can I be tested on this topic in the PMP exam?”
Situational or Scenario-Based PMP Exam Questions
The PMP exam does not use formatting for critical words. So for example you will never see EXCEPT or except on the exam. It will always be written simply as except.
Most questions on the PMP exam are situational or scenario-based. These questions test your ability to apply theoretical expertise to real-life project management situations. These questions may be short (one or two sentences) or could be long-winded (a whole paragraph). The idea behind longer questions is that in real life, you are often provided with both relevant and irrelevant information. Your task is to identify what is important, ignore what does not matter, and then act upon the real issues. Be sure to read and accurately understand what is asked in a PMP exam question.
A single word can be critical, such as NOT or EXCEPT or ONLY or ALWAYS, which can change the meaning of the question or an answer choice.
Often, situational questions will have two choices, which may appear to be reasonably correct. Therefore, it is vital that you identify what the question is actually asking. Based on the question and your knowledge of project management concepts, you must find the BEST answer. It will not always be the ideal/perfect answer you would prefer to see as the correct choice. Sometimes you will have to eliminate the worst three choices and stay with a bad one, but it should be BETTER than the others, the lesser of four evils if you wish. Other times, all four choices may seem correct, so, again, you would have to select the one that is better than the others.
Here is a situational sample question:
-
During project execution, several unexpected issues have developed and are now threatening the project schedule and budget.
What is the best course of action for the project manager to address the issues?
A. Use contingency reserves
B. Review project funding requirements
C. Use management reserves
D. Review organizational process assets -
Correct Answer: C. Use management reserves
Explanation:
The total project budget includes the cost baseline plus the management reserves. The cost baseline is comprised of the work package estimates and contingency reserves. The contingency reserves are allocated for identified risks. Management reserves are withheld for unforeseen risks that affect the project. According to the scenario, the issues developed during the project were unexpected. Therefore, of the choices provided, using the management reserves is the best course of action for the project manager.Note, the scenario describes issues, while the explanation refers to risks. Prospective PMP aspirants should keep in mind that the questions on the real PMP exam may have such discrepancy in their wording.
A final tip on the situational PMP questions, try not to overthink the situation. A real-life situation may have a multitude of factors and considerations that cannot be represented in a single exam question. Try not to think of too many “what if”, “what about” scenarios or fixate that “this would never happen in the real world.” Remember that a situational question aims to test how you apply the theoretical knowledge. Focus on answering the question with the given information, your project management experience, and knowledge gained during the exam preparation.
And if you want to practice the most difficult PMP exam questions that the vast majority of students get wrong, check out our best-selling book, The 50 PMP Exam Prep Questions Everyone Gets Wrong.
Knowledge-Based PMP Exam Questions
The number of knowledge-based questions on the PMP exam is relatively low, and answering them may not be that difficult if you know or remember the project management concepts outlined in the PMBOK® Guide. These questions may be based on your knowledge of the project management principles, project performance domains, processes, or, in some cases (although rare), the inputs, outputs, tools and techniques, also known as ITTOs.
Do you know this?
-
A project is in its initial planning. Due to the nature of the project, the project manager needs to develop a highly detailed project scope statement.
Which of the following elements should be included? (Choose three.)
A. A description of the deliverables that will need to be produced to complete the project
B. The conditions that are required to be met before deliverables are accepted
C. The conditions to be met in order to close or cancel the project
D. A hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team
E. The identification of what will be out of the project scope
F. The assigned project manager, responsibility, and level of authority -
Correct Answers:
A. A description of the deliverables that will need to be produced to complete the project
B. The conditions that are required to be met before deliverables are accepted
E. The identification of what will be out of the project scopeExplanation:
The project scope statement provides a description of the project scope, major deliverables, and exclusions. The elements typically included in the project scope statement include the project scope description, deliverables, acceptance criteria, and project exclusions. The correct answer choices describe the deliverables, acceptance criteria, and project exclusions. The incorrect answer choices represent elements that should be included in the project charter or describe the work breakdown structure (WBS).
Watch this Video with a Knowledge-Based Sample PMP Exam Question
Click the image below to watch a video where we review a knowledge-based PMP question. It discusses the topic of cognitive bias. In the video you first see the question, then you have 30 seconds to find the correct answer, and then we reveal the solution and explain the correct answer:
Students both love and hate these knowledge based PMP exam questions. Some students like these questions because if you study the PMBOK® Guide well, you should be able to handle the majority of these knowledge-based questions easily. Students who lack preparation do not like this type of questions, since they can easily be confused by unfamiliar terminology. You also have to watch out for questions that are not directly covered in the PMBOK® Guide.
Interpretational PMP Exam Questions
Interpretational questions test your ability to deduce a situation or condition from the description of a status or problem. So for example, in a PMP exam question, you may be provided a graph or performance metric, where you have to be able to determine if a good, bad or neutral/indifferent interpretation applies.
How would you interpret this sample question?
-
You have been requested to fill in for a project manager who has called in sick midway into project execution. As you get yourself familiar with the project team, you are impressed to see how well the team members collaborate and work through issues smoothly and effectively.
Based on your observations, where is the team on the Tuckman ladder?
(On the actual PMP exam, you will be requested to click the correct area in the image. But here in the simulator, please select the answer below.)
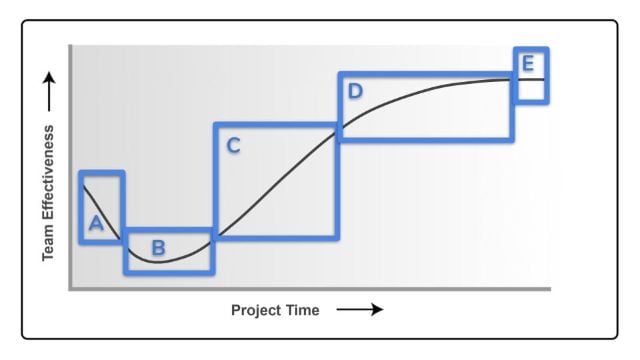
A. Area A
B. Area B
C. Area C
D. Area D
E. Area E -
Correct Answer: D. Area D
Explanation:
The Tuckman ladder is one of the models used to describe stages of team development. This model is typically referred to by project management practitioners as part of the Develop Team process. The model includes five stages: forming, storming, norming, performing, and adjourning. While it is safe to say that most teams go through all five stages, some may get stuck in a particular stage or even regress (go back) to an earlier stage. On the other hand, projects with team members who worked together in the past might skip a stage. Each stage is distinguished by different dynamics among the team members resulting in various levels of team effectiveness. Team effectiveness is at its lowest level during the storming stage as the environment is characterized by a high degree of conflict and a lack of collaboration among the team members. As the team members begin to work together and trust each other, in other words, the relationships between the team members normalize (thus the name of the next stage, norming), the degree of team effectiveness increases. Teams that successfully go through the norming stage would eventually reach the performing stage, which is the highest level of team development. In the performing stage, the team function as a well-organized unit, and the team effectiveness is at its highest.Area D represents the performing stage of the team development model, where the team's performance is at its highest level. Teams that reach this level of development, function as well-organized units. The team members are interdependent and work through issues smoothly and effectively. The scenario closely matches this description, making performing the best answer to the question asked.
Formula-based questions (described later in this article) could also be interpretational rather than computational. For example, "The project CPI is 0.87. What does it mean for the project?"
A good place to start is Table 7-1. Earned Value Calculations Summary Table on page 267 of the PMBOK® Guide, Sixth Edition. Yes, this Edition is still relevant, and you can access it online, using the new PMI digital platform PMIstandards+TM. In addition to mastering formulas and how they are used, focus on the last column of the table, called "Interpretation of Result" as it will help you answer formula-based interpretational PMP exam questions.
Technique-Based PMP Exam Questions
According to the PMBOK® Guide, a technique is "a defined systematic procedure employed by a human resource to perform an activity to produce a product or result or deliver a service, and that may employ one or more tools."
Almost every project management process or performance domain in the PMBOK® Guide has corresponding tools and techniques. Therefore, you will likely encounter a question on your PMP exam that tests your understanding of a specific tool or technique. It may be a knowledge-based question where you can demonstrate your understanding of what a tool/technique is used for, an application-based question testing your skills of how the tool/technique is utilized, or an interpretational question that describes a situation and requires you to identify the tool/technique implied by the scenario.
Do you know this technique for your PMP Exam?
-
A project manager meets with a customer for initial discussions about an upcoming project. At the end of the meeting, the customer asks the project manager for a rough estimate of the project duration. Based on her experience with three similar projects, the project manager provides an estimate of 8-10 months.
What estimation technique does the project manager use?
A. Expert judgment
B. Three-point estimating
C. Analogous estimating
D. Bottom-up estimating -
Correct Answer: C. Analogous estimating
Explanation:
The project manager is using historical duration information from comparable projects to estimate the duration of a future project. This gross value estimating approach is called analogous estimating and is frequently used to provide a ballpark figure when there is a limited amount of detailed information available about the project.
Our best advice is to go through the sections of the PMBOK® Guide that describe the various tools, techniques, models, methods, and artifacts and understand each one of them, its purpose, and how it is applied. Some are easier to grasp. For example, brainstorming is familiar and intuitive, and most students probably have used this technique on their projects. However, understanding the Stacey Complexity Model used to determine the relative complexity of a project requires more study and practice.
Formula-Based PMP Exam Questions
Earned Value Management (EVM or EV) is extremely important for the PMP Exam. You must know and be able to apply the EVM formulas masterfully.
Based on feedback from our students, there are very few formula-based questions on the PMP exam, and even those are relatively easy, mainly requiring you to perform a simple calculation or interpret its result. But do you want to risk it and skip studying formulas? After all, scoring a few more points by correctly answering these questions is what can help you pass your PMP exam.
Therefore, knowing PMP exam formulas backward and forwards and understanding each element of the formulas would give you critical decision-making criteria to know how to apply them and interpret their results. A good grasp of the formulas also may help you more easily eliminate answer choices that clearly cannot be correct based on your understanding of the formulas.
Here is a sample PMP exam question with a formula for you:
-
You are managing a renovation project of a house which is to be completed at a budget of $100,000. Earned value analysis shows that so far you have completed 40% of the work and spent $60,000.
How much more will it cost to complete the project if the cost performance remains unchanged?
A. $160,000
B. $149,254
C. $120,000
D. $89,254 -
Correct Answer: D. $89,254
Explanation:
The total budget, or budget at completion (BAC), is $100,000. The cost so far, or actual cost (AC), is $60,000. You have completed 40% of the work which is the earned value (EV), i.e., EV = 40% x $100,000 = $40,000.Understanding what exactly the question asks is the key to answering the question correctly. The last sentence of the question starts with "How much more will it cost to complete the project...", implying we are requested to find the estimate to complete (ETC). The ETC can be calculated as follows:
ETC = EAC - AC, where the EAC is the estimate at completion.
Selecting the correct formual for the EAC is another key to answering this question correctly. The last sentence ofthe question ends with "...if the cost performance remains unchanged?", implying that the formula for the EAC should consider the cost performance index (CPI), i.e.:
EAC = BAC / CPI
The CPI, in turn, can be claculated using the following formula:
CPI = EV / AC = 40,000 / 60,000 = 0.67
The rest of the calculations are shown below:
EAC = 100,000 / 0.67 = 149,254
ETC = 149,254 - 60,000 = 89,254
Therefore, the cost to complete the renovation if the cost performance remains unchanged is $89,254
There is really only one way to prepare yourself for formula-based questions on the exam: You have to study and practice all the formulas. And so you must know nearly fifty formulas, twenty important values and close to thirty formula-related acronyms. You have to be able to apply the formulas to a project scenario, and if I give you the result of a formula, then you must be able to interpret what that figure means for your project.
But here is the good news... Formula-based questions only have one correct answer. Those PMP exam questions that ask you to select "the best" action or "the next" action often have two or even three answers that seem possible. Not so with the formula questions. Once you know your formulas and understand how to correctly apply them in a given situation, then there is only one correct answer. Because 1 + 1 = 2. Period.
To practice more formula-based questions and go above and beyond in your PMP exam preparation, check out our new book called The PMP Exam Formula Study Guide. It contains 160 computational and interpretational questions. The book is not just a collection of questions; it is a comprehensive guide that will teach you tips and tricks of answering formula-based questions on your PMP exam. The 160 questions are exclusive to the book and not part of the exam simulator. The book is fully updated for the current exam, with a special focus on the interpretational questions to make sure you learn what you need to pass.
My Top 10 Recommended Web Sites for Free PMP Exam Questions
I have done my own research on free PMP exam sample questions. I can tell you, that there are many free resources readily available that can help you get you started. I have narrowed it down to a list of 10 that I recommend.
The best websites for PMP Exam Sample Questions
-
Take a sample exam with 120 questions from our simulator.
-
I recorded a series of PMP exam questions as short videos. Each video looks at one question and I explain the correct answer. A great way of learning.
-
75 free PMP sample questions. List of other links to over 3000 questions.
-
70 free PMP sample questions with an additional 28 questions. Filter questions by knowledge area. Additional 200 question practice exam.
-
Over 1,000 free PMP sample questions. Includes flashcards and dictionary
-
20 free PMP sample questions
-
200 free PMP sample questions per exam. Access 2 exams.
-
Four 50-question quizzes with immediate results and explanations.
-
50 free PMP exam sample questions. You need to register to review your results.
-
Get 69 questions in 3 exams. PMP exam questions. Take exam in Real Exam Mode. With option to take in Timed Mode or Learning Mode where you can see hints or opt to take fewer questions per session. Disclaimer: This is my own simulator!
You can see that apart from the link, I have tried to give you an idea of how many questions are available and key features of each website. You can see for yourself that the websites differ in terms of the number of questions that they offer as well the level of sophistication in presenting students the free PMP exam sample questions. Some providers list all the free PMP exam sample questions at once; others deliver only a question a day. You may receive an email with the PMP questions, or you may have to register to answer PMP exam sample questions in a PMP exam simulator environment.
The Next Step for PMP Certification Exam Prep
Find even more free resources and important information on how to prepare for the PMP exam on the free section of the PM PrepCast website. I encourage students to try to answer as many practice exams under real exam conditions. In other words, do not refer to your notes or the PMBOK® Guide, take a full exam within the time limit.
Learn More about PMP Exam Questions
- Types of PMP Exam Questions You Should Know To Pass The PMP Exam
More about the types of questions you have to know for the exam. Includes PMBOK® Guide knowledge questions. - How to Find the Best Answers for the PMP Exam Questions to Become a Certified PMP
Knowing the questions types is not enough. You need to be able to find the correct answer, too! - Create Your Own PMP Exam Sample Questions to Prepare for the PMP Exam
Make your own questions and strengthen your understanding of the topics.
Conclusion and Recommendation
If you get below average results on your exam simulator, then consider getting more training from The PM PrepCast with over 40 hours of audio and video lessons. For best ROI on your investment, choose the "Elite", which includes both The PM PrepCast and PM Exam Simulator.
As I said, practice makes perfect. Free PMP exam questions and knowing what type of questions to expect on the exam are great for starters. However, in order to better prepare for your PMP exam, you want to practice your exam realistically. After all, you don't practice for your driving test in a bumper car. No. You drive a real car out on the streets to gain driving experience.
And so the best way to prepare for your PMP exam is to practice with a real PMP Exam Simulator.
By using a PMP Exam Simulator you will be better and better prepared for your exam: You learn what it feels like to take a complete, 180-question, almost a 4-hour long exam. You get to apply your knowledge and experience to hundreds of simulated exam questions. And, if you answer a question incorrectly, you can see why you got it wrong and will learn from the mistake. A simulator is a must-have.
Will any simulator do? Probably.
Most simulators that you will find in the current market are of a good quality. But of course, I am biased and I prefer my own PMP Exam Simulator. It offers 2,070+ high-quality questions with detailed explanations and references alongside every answer (correct and incorrect!), so you can understand why your answer is or is not correct. But don't just believe me -- instead read PMP Exam Simulator Reviews from our former students. Remember you can always try the free version first. No strings attached.
© 2015-2023 OSP International LLC. All rights reserved. This copyrighted article may not be reproduced without express written consent of OSP International LLC.


